Consolidating Student Loans Specific Strategies and Options
A specialized guide to consolidating student loans including federal and private loan options and strategies.

A specialized guide to consolidating student loans including federal and private loan options and strategies.
Consolidating Student Loans Specific Strategies and Options
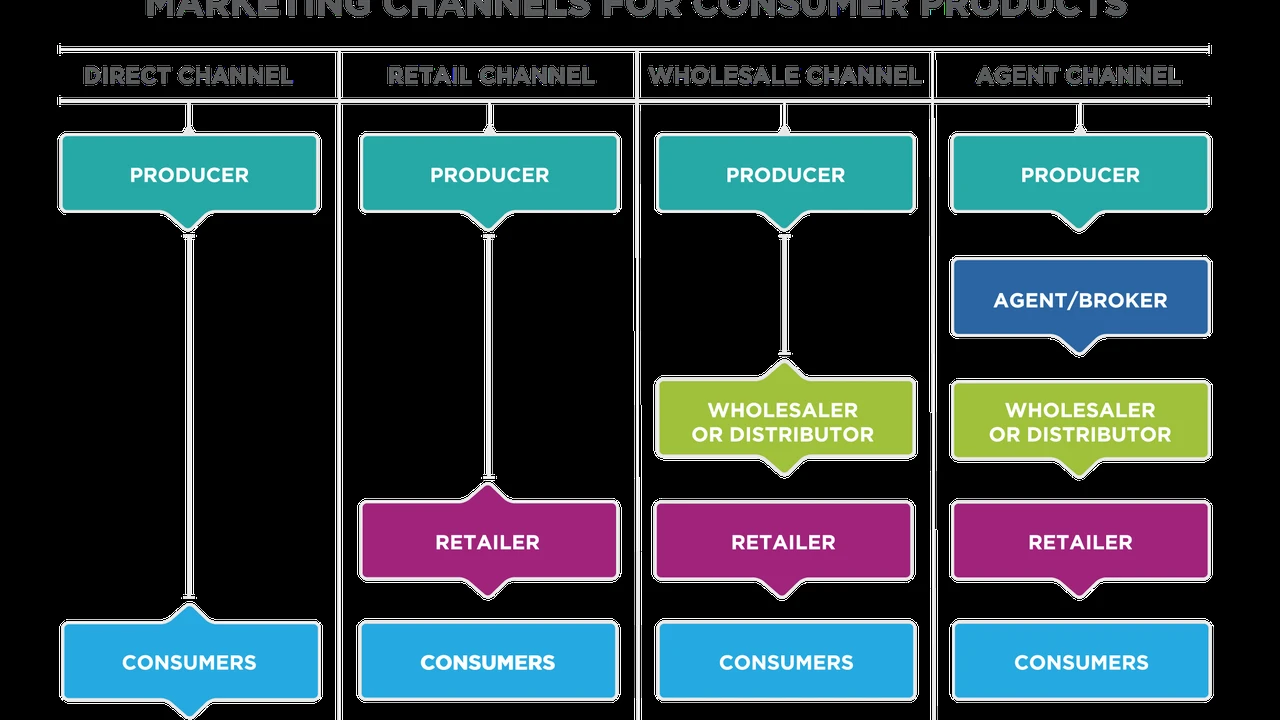
Student loan debt is a significant burden for millions of people across the United States and increasingly in Southeast Asian countries like the Philippines and Malaysia. Whether you're fresh out of college or have been navigating repayment for years, the sheer volume of loans, varying interest rates, and multiple due dates can feel overwhelming. This is where student loan consolidation comes into play – a powerful strategy designed to simplify your repayment process, potentially lower your monthly payments, and even reduce the total interest you pay over time. But unlike other forms of debt consolidation, student loan consolidation has its own unique set of rules, especially when distinguishing between federal and private loans. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from understanding your options to choosing the right path for your financial future.
Understanding Federal Student Loan Consolidation Benefits and Eligibility
Federal student loan consolidation is a program offered by the U.S. Department of Education that allows you to combine multiple federal student loans into a single Direct Consolidation Loan. This isn't about getting a new loan from a private lender; it's about streamlining your existing federal debt under one new federal loan. The primary benefit here is simplification: instead of juggling several payments to different servicers, you'll have just one monthly payment. But the advantages extend beyond mere convenience.
Key Benefits of Federal Student Loan Consolidation for Borrowers
- Simplified Payments: One loan, one servicer, one monthly payment. This significantly reduces the chances of missing a payment and incurring late fees.
- Access to Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans: Some federal loans, particularly older ones like FFEL Program loans, might not be eligible for all IDR plans. Consolidating them can open up access to options like Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR), which can dramatically lower your monthly payments based on your income and family size.
- Access to Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Similarly, certain older federal loans might not qualify for PSLF. Consolidating them into a Direct Consolidation Loan makes them eligible, provided you meet all other PSLF requirements.
- Extended Repayment Period: You can extend your repayment term up to 30 years, which will lower your monthly payment. However, be aware that this also means you'll pay more interest over the life of the loan.
- Fixed Interest Rate: The interest rate on a Direct Consolidation Loan is the weighted average of the interest rates on the loans being consolidated, rounded up to the nearest one-eighth of one percent. This provides predictability, as your rate will be fixed for the life of the loan.
Eligibility Requirements for Federal Student Loan Consolidation
To be eligible for a Direct Consolidation Loan, most federal student loans qualify, including Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, FFEL Program loans (Subsidized, Unsubsidized, PLUS), Perkins Loans, and more. Generally, loans must be in repayment or in their grace period. If a loan is in default, you might still be able to consolidate it if you agree to repay the new Direct Consolidation Loan under an income-driven repayment plan or make three consecutive, voluntary, on-time full monthly payments on the defaulted loan before consolidating.
Exploring Private Student Loan Refinancing A Different Approach
It's crucial to understand that federal student loan consolidation is distinct from private student loan refinancing. You cannot consolidate federal and private loans together into a Direct Consolidation Loan. If you have private student loans, or if you want to consolidate federal loans with private loans, you'll need to explore private student loan refinancing. This involves taking out a new loan from a private lender to pay off your existing student loans (both federal and/or private).
Key Benefits of Private Student Loan Refinancing for Borrowers
- Potentially Lower Interest Rates: This is often the biggest draw. If your credit score has improved significantly since you took out your original loans, or if market interest rates have dropped, you could qualify for a much lower interest rate, saving you thousands over the life of the loan.
- Simplified Payments: Like federal consolidation, refinancing combines multiple loans into one, simplifying your monthly payments.
- Flexible Repayment Terms: Private lenders often offer a range of repayment terms, from 5 to 20 years, allowing you to choose a monthly payment that fits your budget.
- Release of Co-signer: Some lenders offer co-signer release options after a certain number of on-time payments, which can be a huge relief for both the borrower and the co-signer.
Risks and Considerations for Private Student Loan Refinancing
While attractive, private refinancing comes with significant trade-offs, especially if you're refinancing federal loans:
- Loss of Federal Loan Benefits: This is the most critical point. When you refinance federal loans with a private lender, you permanently lose access to all federal benefits, including income-driven repayment plans, deferment and forbearance options, and Public Service Loan Forgiveness. This is a major decision that should not be taken lightly.
- Credit Score Dependent: Your eligibility and interest rate for private refinancing are heavily dependent on your credit score and income. If your credit isn't excellent, you might not qualify for the best rates.
- No Standardized Protections: Private loans generally offer fewer consumer protections compared to federal loans.
Top Private Lenders for Student Loan Refinancing A Comparative Look
If you've weighed the pros and cons and decided private refinancing is right for you, here are some of the leading lenders to consider. Remember, rates and terms vary widely based on your creditworthiness, so it's essential to get personalized quotes.
Sofi Student Loan Refinancing
- Overview: SoFi is one of the pioneers in online student loan refinancing, known for its competitive rates and a wide range of loan products. They offer both fixed and variable interest rates.
- Target Audience: Borrowers with strong credit scores, stable income, and a good payment history. They often cater to high-earning professionals.
- Key Features: No origination fees, no prepayment penalties, unemployment protection, and career support services. They also offer a co-signer release option.
- Typical Rates: Variable rates often start below 3% APR, fixed rates can be found from around 4% APR, depending on market conditions and borrower profile.
- Use Case: Ideal for someone with excellent credit looking to significantly lower their interest rate and simplify payments, willing to forgo federal protections.
Earnest Student Loan Refinancing
- Overview: Earnest stands out for its highly personalized approach to refinancing. They consider more than just your credit score, looking at your savings, spending habits, and education.
- Target Audience: Responsible borrowers with good financial habits, even if their credit score isn't perfect.
- Key Features: Flexible payment options (you can choose your exact payment amount), ability to skip one payment per year (with interest accrual), no fees, and a co-signer option.
- Typical Rates: Similar to SoFi, competitive variable rates starting around 2.5% APR and fixed rates from 3.5% APR.
- Use Case: Great for borrowers who want a highly customized repayment plan and appreciate a lender that looks beyond traditional credit metrics.
CommonBond Student Loan Refinancing
- Overview: CommonBond offers a strong combination of competitive rates, excellent customer service, and a social mission (they fund a child's education in a developing country for every loan funded).
- Target Audience: Graduates from eligible universities, often with strong credit.
- Key Features: Fixed, variable, and hybrid interest rate options. They also offer forbearance and a co-signer release option.
- Typical Rates: Variable rates from 2.75% APR, fixed rates from 3.75% APR.
- Use Case: A good choice for borrowers seeking competitive rates and a lender with a social impact, particularly if they attended a qualifying institution.
Splash Financial Student Loan Refinancing
- Overview: Splash Financial is a marketplace that connects borrowers with a network of lenders, allowing you to compare offers from multiple banks and credit unions with a single application.
- Target Audience: Borrowers looking for the best possible rate by comparing multiple offers without multiple applications.
- Key Features: Access to a wide range of lenders, including some that specialize in specific professions (e.g., medical residents). No fees.
- Typical Rates: Rates vary widely as they are a marketplace, but they aim to find you the lowest available rates from their partners.
- Use Case: Excellent for those who want to shop around efficiently and find the absolute lowest rate available to them.
LendKey Student Loan Refinancing
- Overview: LendKey also operates as a marketplace, but it focuses specifically on connecting borrowers with credit unions and community banks, which often offer more personalized service and potentially lower rates.
- Target Audience: Borrowers who prefer working with smaller, local financial institutions and are looking for competitive rates.
- Key Features: Access to a network of credit unions and banks, no origination fees, and flexible repayment terms.
- Typical Rates: Competitive rates, often starting from 2.99% APR for variable and 3.99% APR for fixed.
- Use Case: Ideal for borrowers who value the credit union experience and want to explore options beyond large national banks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Consolidating or Refinancing Your Student Loans
Navigating the process can seem daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes it much clearer.
Step 1 Evaluate Your Current Loan Portfolio and Financial Situation
Before you do anything, gather all your loan information: loan types (federal vs. private), current interest rates, outstanding balances, loan servicers, and repayment terms. Understand your current monthly payments and how they fit into your budget. Assess your credit score – this is crucial for private refinancing. For federal loans, consider if you rely on or anticipate needing federal benefits like IDR or PSLF.
Step 2 Determine if Federal Consolidation or Private Refinancing is Right for You
This is the most critical decision. If you have only federal loans and want to simplify payments, access IDR plans, or qualify for PSLF, federal consolidation is likely your best bet. If you have private loans, or if you have excellent credit and are willing to give up federal protections for a potentially lower interest rate, private refinancing is the path to explore. If you have both, you might consider federal consolidation for your federal loans and private refinancing for your private loans, or private refinancing for all of them if you're comfortable losing federal benefits.
Step 3 For Federal Consolidation Apply Through StudentAid gov
The application for a Direct Consolidation Loan is straightforward and can be completed online at StudentAid.gov. You'll need to select the loans you wish to consolidate and choose a repayment plan. The process typically takes a few weeks to complete.
Step 4 For Private Refinancing Shop Around and Compare Offers
Don't just go with the first lender you find. Use marketplaces like Splash Financial or LendKey, or apply directly to a few top lenders like SoFi, Earnest, and CommonBond. Most lenders offer a pre-qualification process that allows you to see your potential rates without impacting your credit score. Compare interest rates (fixed vs. variable), repayment terms, fees (origination, prepayment), and any borrower protections or benefits offered.
Step 5 Review Loan Terms and Finalize Your Application
Once you've chosen a lender, carefully review the loan agreement. Understand the interest rate, monthly payment, total cost of the loan, and any fine print. Ask questions if anything is unclear. Once satisfied, sign the agreement.
Step 6 Manage Your New Consolidated or Refinanced Loan
After your new loan is disbursed and your old loans are paid off, set up automatic payments to avoid missing due dates. Keep track of your new loan servicer and access your account regularly to monitor your progress. If you chose private refinancing, remember you've lost federal protections, so build up an emergency fund to cover unexpected financial hardships.
Special Considerations for Student Loan Consolidation
Beyond the basic steps, there are a few nuances and specific scenarios to keep in mind.
Consolidating Parent PLUS Loans
Parent PLUS loans are federal loans taken out by parents to help pay for their child's education. While they can be consolidated into a Direct Consolidation Loan, the parent remains responsible for the debt. Consolidating Parent PLUS loans can make them eligible for the Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) plan, which is the only IDR plan available directly to Parent PLUS borrowers. If a parent wants access to other IDR plans, they would need to consolidate the Parent PLUS loan into a Direct Consolidation Loan, and then consolidate that Direct Consolidation Loan again with at least one of their own federal student loans (if they have any). This is often referred to as the 'double consolidation' loophole, though it's a complex strategy.
The Impact of Consolidation on Loan Forgiveness Programs
For federal loans, consolidating generally resets the clock on any progress towards loan forgiveness programs like PSLF or IDR forgiveness. However, recent changes (like the IDR Account Adjustment) may allow past payments on consolidated loans to count towards forgiveness, so it's crucial to stay updated on federal student aid policies. Always check the latest guidance from StudentAid.gov.
When Not to Consolidate Federal Loans
There are situations where federal consolidation might not be beneficial. If you have a very low interest rate on one of your existing federal loans, consolidating it with higher-rate loans might slightly increase its effective rate. Also, if you're very close to qualifying for PSLF or IDR forgiveness on your existing loans, consolidating could reset your payment count, delaying forgiveness (though, as mentioned, recent adjustments might mitigate this for some). Always calculate the weighted average interest rate before consolidating.
Student Loan Consolidation in Southeast Asia A Growing Trend
While the specifics of federal student loans are unique to the U.S., the concept of consolidating debt, including education loans, is gaining traction in Southeast Asian markets. Countries like the Philippines, Malaysia, and Singapore are seeing an increase in private financial institutions offering personal loans or specific education loan refinancing products that function similarly to private student loan refinancing in the U.S.
Philippines Student Loan Consolidation Options
In the Philippines, government-backed student loan programs are less prevalent than in the U.S. Most student financing comes from private banks or specialized lending institutions. Borrowers often consolidate their education debts through personal loans from banks like BDO, BPI, or Metrobank. These personal loans can be used to pay off multiple smaller education-related debts, simplifying payments and potentially securing a lower interest rate if the borrower has a strong credit profile. Interest rates for personal loans in the Philippines can range from 1.5% to 3% per month (18% to 36% APR), so securing a lower rate through consolidation is highly desirable for eligible borrowers.
Malaysia Student Loan Consolidation Options
Malaysia has its own government-backed student loan scheme, PTPTN (Perbadanan Tabung Pendidikan Tinggi Nasional). While PTPTN offers its own repayment schemes, borrowers with multiple private education loans or other debts might look to personal financing from banks like Maybank, CIMB, or Public Bank to consolidate. Islamic personal financing options are also popular, adhering to Sharia principles. Rates for personal loans in Malaysia typically range from 4% to 10% APR for well-qualified borrowers. Some banks might offer specific debt consolidation packages that include education loans.
Singapore Student Loan Consolidation Options
Singaporean students often rely on education loans from major banks like DBS, OCBC, and UOB. For those with multiple loans or high-interest credit card debt alongside education loans, debt consolidation plans (DCPs) are available. These DCPs allow individuals to consolidate unsecured debts, including education loans, into a single loan with a lower interest rate and a fixed repayment period. Eligibility for DCPs is strict, requiring a minimum annual income and a total unsecured debt exceeding 12 times the monthly income. Interest rates for DCPs in Singapore can be quite competitive, often ranging from 3% to 7% APR, making them an attractive option for eligible individuals.
Final Thoughts on Student Loan Consolidation
Student loan consolidation, whether federal or private, is a powerful tool for managing your education debt. It offers the potential for simplified payments, lower interest rates, and a clearer path to financial freedom. However, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. Carefully assess your individual circumstances, understand the differences between federal consolidation and private refinancing, and weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks. By doing your homework and choosing the right strategy, you can take a significant step towards taking control of your student loan debt and building a more secure financial future.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)